Analytics
by Le Thi Anh Hong, Joachim Clemens and Nguyen Thai Hoa.
The estrogenecity of a water sample is detected via the YES assay as described by (Routledge and Sumpter, 1996) using an absorbance microplate photometer (Elisa reader with absorbance at 540nm and 630nm). Figure 1 shows the reaction of the yeast cells on endocrine disruptors, figure 2 a standard curve for 17β- estradiol ranging from 0.1μg/l to 3.5 μg/l. At the moment, the analytical procedure is optimized.
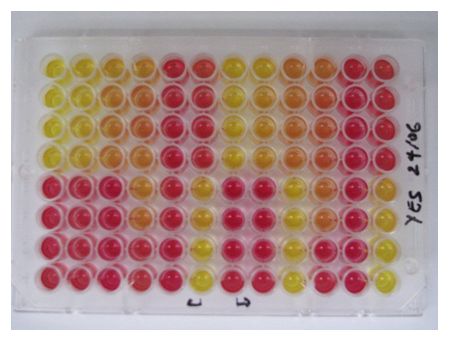
Figure 1: Reaction of yeast cells on endocrine disruptors.
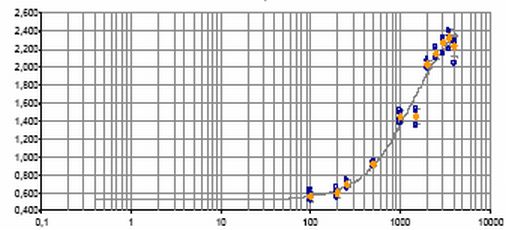
Figure 2: Standard curve for 17β- estradiol.
As we are working closely with the group that monitors pesticides, we were analyzing a set of pesticides on their estrogenicity (propiconazole, alpha endosulphan, beta endosulphan, methamidophos, dimethoate, diazinon, alpha cypermethrin, Fipronil, Imidacloprid). Two of them, Propiconazole and Fipronil showed a positive estrogenic response.
Literature
Routledge EJ, Sumpter JP (1996): Estrogenic activity of surfactants and some of their degradation products assessed using a recombinant yeast screen; environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, Vol. 15 ,No. 3, 241-248.
Sonoko Yamaguchi, Aki Ito, Toshitsugu Higashino, Chiemi Miura, Tetsuro Agusa, Reiji Kubota, Hisato Iwata, Shinsuke Tanabe, and Takeshi Miura (2004). Influence of endocrine disruptors on reproductive of aquatic animals in Indochina.
Proceedings of the International Symposium on the Development of Water Resource Management System in Mekong Watershed, December 3rd-4th, 2004, Hanoi, Vietnam, pp 32-40.




