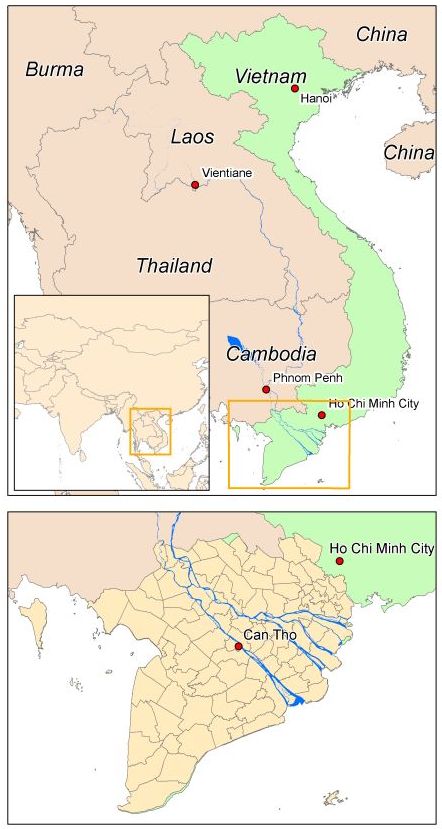
The Mekong Delta, Vietnam
|
The Mekong Delta (Vietnamese: đồng bằng sông Cửu Long “Nine Dragon river delta”) is the region in southwestern Vietnam where the Mekong River approaches and empties into the sea through a network of distributaries. The Mekong delta region encompasses a large portion of southeastern Vietnam of 39,000 km². The area covered by water depends on the season.
The complex water regime of the Delta
The climate in the Mekong Delta is influenced by both the southwest and northeast monsoons. In general the dry season runs from December to April while the wet season spans May to November. The marked seasonality in rainfall leads to both annual floods and water shortages in the Delta. In the wet season almost 50% of the Delta is flooded (1,900 km2). In the dry season, flow in the Mekong is insufficient to prevent saline intrusion and extensive salinization of waterways occurs in the lower Delta. The whole of the Ca Mau Peninsula in the Delta’s southwest is salinized for 6 months during the dry season as there is insufficient freshwater flow in the Mekong to displace saline intrusion from the southwestern sector of the Delta. Wet season floods and dry season saline intrusion are two of the main hydrologic problems of the Delta.
Rising demands of an aspiring country
The main current environmental issues in the Delta closely link to water usage, particularly regarding availability of water for agriculture, but also from flooding, storage and release of water from hydropower dams from upstream riparian countries. High population growth is leading to increasing demand of drinking water, land for agriculture and construction. Water quality of the Mekong is affected by such factors as industrial pollution, urban waste disposal and sewage, use of fertilisers and pesticides, soil erosion and salt water intrusion. In rural areas only a minority of the population have access to clean drinking water Chemical and organic pollution pose serious threats to human health and the environment. Human pressure on mangroves, forests and wetlands is deteriorating natural coastal protection, fisheries and biodiversity. Furthermore, increasing severity of flood events causes high damages in agriculture, infrastructure and above all the endangerment especially of the rural population.
Key issues of the Delta
|
Overview map of the project area. |